Low Histamine Diet
What Is the Low Histamine Diet?
Histamine is a natural chemical present in our bodies and in certain foods. It is present in our skin, gastrointestinal tract, heart, lungs and brain.
Someone with histamine intolerance may benefit from a low histamine diet. Consuming foods that are low in histamine helps to reduce the overall “load” of histamine in the body and may alleviate symptoms.
Histamine acts as a neurotransmitter (chemical messenger) in the central nervous system. It is also involved in the secretion of stomach acid. Histamine is produced by mast cells during immune responses to allergens.
When histamine creates an allergic response, a person may experience typical allergy symptoms like congestion or runny nose, watery eyes, itchy skin rashes, sneezing, swelling, and inflammation or headaches. An abundance of histamine in the gut may cause gastrointestinal symptoms.
Histamine intolerance is when there is too much histamine in the body. This excess can be caused by:
Exposure to an allergen
Consuming high histamine foods
Impaired breakdown of histamine (due to genetic factors, certain medications, or poor gut health)
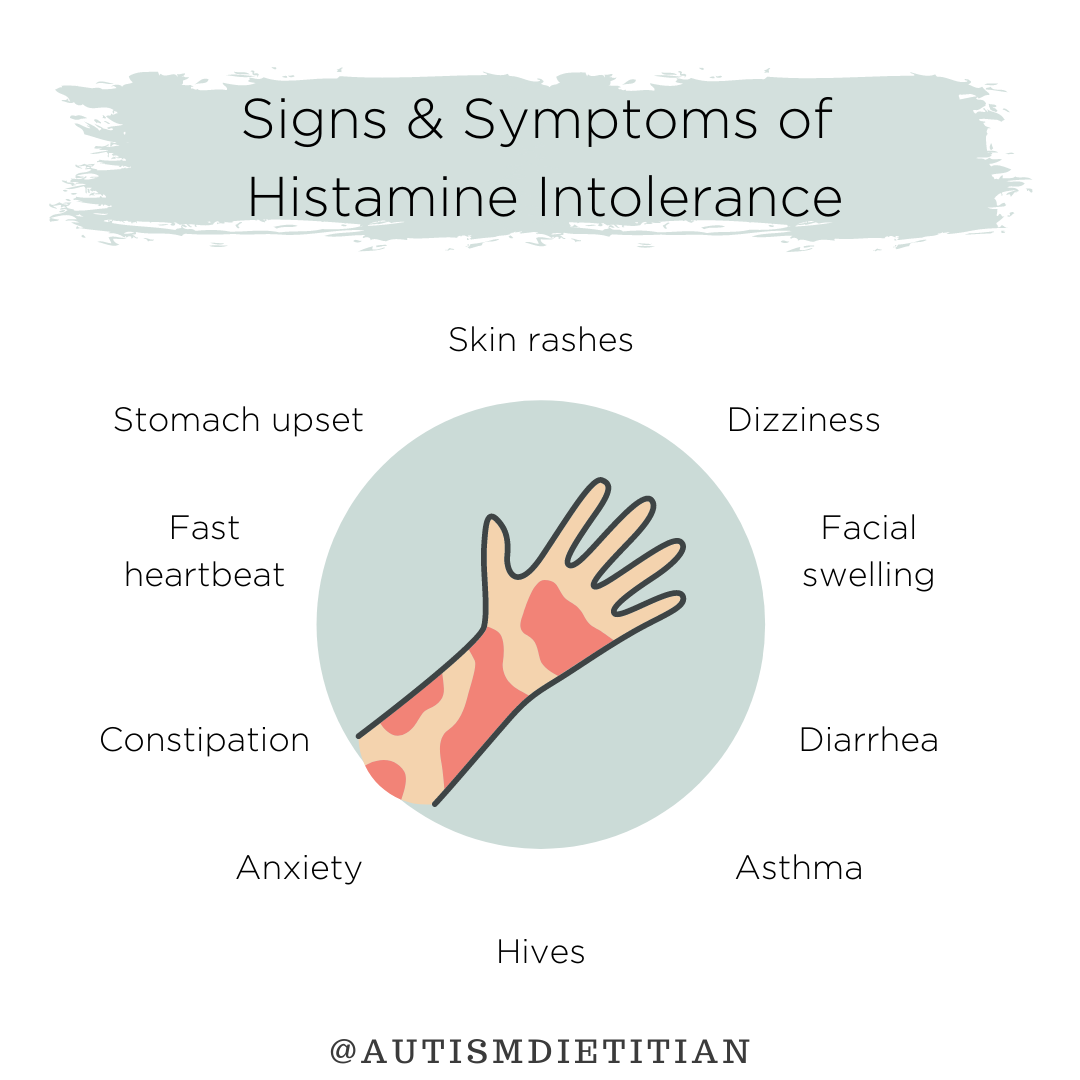
Histamine intolerance can manifest in a variety of ways including: diarrhea, constipation, stomach cramping, headaches, facial swelling, skin rashes, asthma, dizziness, anxiety, blood pressure changes, or fast/irregular heartbeat.[15]
Someone with histamine intolerance can benefit from a low histamine diet. Consuming foods that are low in histamine helps to reduce the overall “load” of histamine in the body and may alleviate symptoms.
Signs/Symptoms of Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance can manifest in a variety of ways including [15]:
Stomach cramping
Headaches
Facial swelling
Skin rashes
Asthma
Dizziness
Blood pressure changes
Fast/irregular heartbeat
Recommended Foods
Low histamine foods include:
Fresh eggs, meat, and fish that is not leftover or thawed slowly
Fresh dairy products like milk, butter, or soft cheeses like mozzarella, ricotta
Gluten-free grains
All fresh or frozen vegetables except those listed above
Vegetable oils or animal fats
Fresh or dried herbs
Herbal teas
Non-dairy milk like almond or coconut
Most fresh or frozen fruits (some fruits don’t contain histamine but are limited on a low histamine diet. For a more complete list of foods for those following a low histamine diet, visit here.
Foods to Avoid
Foods that are high in histamine include: [2]
Fermented or pickled foods like vinegar, yogurt, kombucha, kefir, sauerkraut, pickles, soy sauce, Worcestershire sauce
Alcohol, especially red wine
Leftover meat, fish, and seafood
Smoked, cured, and aged meats
Aged cheeses
Canned foods
Dried fruits and overripe fruits
Certain vegetables like olives, eggplant, spinach, and tomatoes
A person on a low histamine diet may want to avoid foods that are metabolized using the DAO enzyme. We want the DAO enzyme to be available to break down histamine and not be otherwise occupied. The DAO enzyme will preferentially degrade the foods listed below, so those on a low histamine diet may way to avoid or limit these foods:
Raspberries
Other foods are not necessarily high in histamine but cause histamine to be released from our body’s own mast cells. These are known as histamine liberators and should be avoided or limited on a low histamine diet as well. Histamine liberators include:
Alcohol
Nuts (walnut, cashews)
Seafood, shellfish
Chocolate
Tomatoes, ketchup, tomato juice
Citrus fruits
Some foods also block the DAO enzyme, interfering with the breakdown of histamine.
Alcohol
Tea
Energy drinks
Lifestyle Considerations for Low Histamine Diet
Histamine intolerance can be triggered by yeast/candida and mold. Candida and mold can lead to overall inflammation and GI dysfunction.
Ask your doctor about testing for DAO deficiency and DAO gene polymorphism.
Supplement Recommendations for Low Histamine Diet
DAO enzyme supplements may be helpful
A probiotic with bacterial strains that don’t produce histamine
Certain micronutrients help degrade histamine, including:
Gut healing supplements
Helpful Resources
Websites:
https://www.histamineintolerance.org.uk/about/the-food-diary/the-food-list/
https://www.functionalnutritionanswers.com/low-histamine-diet-101-what-to-eat-what-to-avoid-and-why/
Cookbooks:
DISCLAIMER: Before starting any supplement or medication, always consult with your healthcare provider to ensure it is a good fit for your child. Dosage can vary based on age, weight, gender, and current diet.
Low Histamine Diet in the Research
Effectiveness of Low Histamine Diet
A histamine-reduced diet improves symptoms of histamine intolerance. [7, 8, 11, 17]
DAO Supplementation
Oral supplementation with exogenous DAO enzyme from porcine kidney is also being used to enhance the intestinal capacity to degrade dietary histamine. [7, 8, 10, 11, 17, 20]
Low Histamine Diet and Asthma
Higher mean airflow obstruction and a trend for prolonged and more severe symptoms were observed among children with asthma that consumed a high histamine diet. Diet may have an active and direct impact on asthma symptoms. [9]
Low Histamine Diet Food List
Management of histamine intolerance is done with a low-histamine diet, although there is no consensus on the list of foods to be excluded. [10]
A comparative review brought out the great variety in the type of foods that are advised against for histamine intolerant individuals. Only fermented foods were unanimously excluded. The presence of chemicals which may impair histamine degradation by the DAO enzyme at the intestinal level could partly explain the reason why certain foods were also frequently reported in low-histamine diets. [16]
Microbiome and Histamine Intolerance
The altered occurrence of Proteobacteria and Bifidobacteriaceae, reduced alpha-diversity as well as elevated stool zonulin levels suggest a dysbiosis and intestinal barrier dysfunction in histamine intolerant patients, which in turn may play an important role in driving disease pathogenesis. [17]
Histamine Intolerance Symptoms
When patients with histamine intolerance were surveyed, the most common and most serious reported symptom was bloating. Other commonly reported gastrointestinal symptoms were postprandial fullness, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and constipation. [18]
We show that intestinal and extra-intestinal non-celiac gluten sensitivity symptoms are very similar to those which can be found in histamine intolerance. [19]
The symptoms of histamine intolerance, although diverse and hence confusing, are remarkably similar to non-clonal mast cell activation syndrome. [21]
Histamine Intolerance and Children
The clinical picture of histamine intolerance in children is similar to that observed in adults apart from male predominance found in pediatric patients. In children, histamine intolerance most likely co-occurs with allergies and bowel diseases. [22]
The Bottom Line
This diet may be a challenge to follow for some people but it really depends on what the person is accustomed to eating. The biggest challenge is determining if a person’s symptoms are indeed due to histamine intolerance and the research agrees that diagnosis is non-standardized and difficult. For those that have histamine intolerance, the diet is widely accepted as an effective way to lower overall histamine in the body and keep symptoms at bay.
Diet Rating
Rating Scale: 1 - 5 Stars ★
We rate the quality and quantity of the research supporting the efficacy of the diet in improving symptoms as well as the Ease of Adherence, taking into account the cost, resources available, the time required, social acclimation to the diet including options available in restaurants and grocery stores which assist convenience and adherence
Ease of Adherence ★★★
This diet is relatively easy to follow, though the challenge is the lack of consensus on a complete “foods to avoid” list. Those that strictly follow the diet may have more of a challenge, though some people may benefit from less strict implementation of the diet.
Research ★★★★
There is an abundance of research to substantiate the use of a low histamine diet if histamine intolerance is suspected. If a low histamine diet proves beneficial, this is part of the criteria for diagnosis with histamine intolerance.
-
[1] Histaminintoleranz.ch. Accessed May 22, 2021. https://www.histaminintoleranz.ch/downloads/SIGHI-Leaflet_HistamineEliminationDiet.pdf
[2] SIGHI. Dietary change. Histaminintoleranz.ch. Accessed May 22, 2021. https://www.histaminintoleranz.ch/en/therapy_dietarychange.html
[3] Smolinska S, Jutel M, Crameri R, O'Mahony L. Histamine and gut mucosal immune regulation. Allergy. 2014;69(3):273-81.
[4] Thangam EB, Jemima EA, Singh H, et al. The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1873.
[5] Gagic M, Jamroz E, Krizkova S, Milosavljevic V, Kopel P, Adam V. Current Trends in Detection of Histamine in Food and Beverages. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(3):773-83.
[6] Kovacova-Hanuskova E, Buday T, Gavliakova S, Plevkova J. Histamine, histamine intoxication and intolerance. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2015;43(5):498-506.
[7] Lackner S, Malcher V, Enko D, Mangge H, Holasek SJ, Schnedl WJ. Histamine-reduced diet and increase of serum diamine oxidase correlating to diet compliance in histamine intolerance. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;73(1):102-4.
[8] Schnedl WJ, Enko D. Histamine Intolerance Originates in the Gut. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1262.
[9] Vassilopoulou E, Konstantinou GN, Dimitriou A, Manios Y, Koumbi L, Papadopoulos NG. The Impact of Food Histamine Intake on Asthma Activity: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2020;12(11):E3402.
[10] Comas-Basté O, Sánchez-Pérez S, Veciana-Nogués MT, Latorre-Moratalla M, Vidal-Carou MDC. Histamine Intolerance: The Current State of the Art. Biomolecules. 2020;10(8):E1181.
[11] Manzotti G, Breda D, Di Gioacchino M, Burastero SE. Serum diamine oxidase activity in patients with histamine intolerance. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016;29(1):105-11.
[12] Overall, the comparative review brought out the great heterogenicity in the type of foods that are advised against for histamine intolerant individuals. Excluded foods were, in most cases, different depending on the considered diet. Only fermented foods were unanimously excluded.
[13] Gagic M, Jamroz E, Krizkova S, Milosavljevic V, Kopel P, Adam V. Current Trends in Detection of Histamine in Food and Beverages. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(3):773-83.
[14] Kovacova-Hanuskova E, Buday T, Gavliakova S, Plevkova J. Histamine, histamine intoxication and intolerance. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2015;43(5):498-506.
[15] Symptoms. Org.uk. Published November 28, 2011. Accessed May 17, 2021. https://www.histamineintolerance.org.uk/about/symptoms/
[16] Sánchez-Pérez S, Comas-Basté O, Veciana-Nogués MT, Latorre-Moratalla ML, Vidal-Carou MC. Low-Histamine Diets: Is the Exclusion of Foods Justified by Their Histamine Content. Nutrients. 2021;13(5):1395.
[17] Schink M, Konturek PC, Tietz E, et al. Microbial patterns in patients with histamine intolerance. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;69(4):
[18] Schnedl WJ, Lackner S, Enko D, Schenk M, Holasek SJ, Mangge H. Evaluation of symptoms and symptom combinations in histamine intolerance. Intest Res. 2019;17(3):427-33.
[19] Schnedl WJ, Lackner S, Enko D, Schenk M, Mangge H, Holasek SJ. Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: people without celiac disease avoiding gluten-is it due to histamine intolerance. Inflamm Res. 2018;67(4):279-84.
[20] Schnedl WJ, Schenk M, Lackner S, Enko D, Mangge H, Forster F. Diamine oxidase supplementation improves symptoms in patients with histamine intolerance. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2019;28(6):1779-84.
[21] Cimolai N. Comparing histamine intolerance and non-clonal mast cell activation syndrome. Intest Res. 2020;18(1):134-5.[22] Nazar W, Plata-Nazar K, Sznurkowska K, Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz A. Histamine Intolerance in Children: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2021;13(5):1486.